From the moment we are born our pancreas is like a machine on autopilot mode which works silently to do its job meal after meal, day after day!
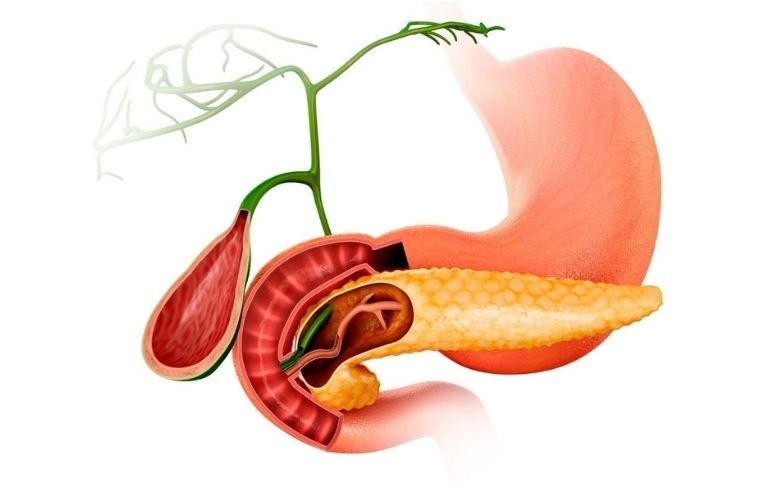
The pancreas is an important organ in the digestive system that resides deep inside your abdomen. It is covered by the stomach and liver.
The pancreas is divided into three anatomical portions: the head, body, and tail. The head of the pancreas is surrounded by the duodenum, which is the upper part of the intestine that connects the stomach to the small intestine. The tail of the pancreas resides in the hilum of the spleen.
The pancreas performs two main functions:
- Exocrine; which releases enzymes to digest the meals
- Endocrine; which releases hormones, insulin, and glucagon to help regulate blood sugar levels
Your pancreas plays an essential role in your body’s digestive system.
It is one of its kind which helps in extracting nutrients, converting food into fuel from the body’s cell without ever breaking down.
Disorders affecting the pancreas include:
– Pancreatitis- Acute or Chronic
– Cysts
– Tumor
– Pancreatic Cancer
– Injury to the pancreas
Each disorder or condition may exhibit different symptoms and requires different treatments.
The prognosis of the treatment of a pancreatic condition depends a lot on factors like the age of the patient, stage of diagnosis, underlying diabetic condition, general health, along with the medical and surgical approach with which it is being managed.
Based upon all these factors a surgeon might make a decision for a patient that, when & which pancreatic surgery procedure is required.
It is located in an anatomically complex region of the body where neighboring organs are closely associated and share the same blood supply.
As a result pancreatic surgeries usually involve the removal of several organs or a part of them together.
With the advent of organ and function preserving procedures, the use of surgical treatment in treating chronic pancreatitis and other less common benign diseases of the pancreas is increasing. Also with the advances in medical and patient care, pancreatic surgery has evolved into a safe procedure with low mortality rates.
World Pancreatic Cancer Day – For more details check out our latest video
INDICATIONS OF PANCREATIC SURGERY:
– To address intractable pain when endoscopic treatment options have been exhausted
– Suspected malignancy
– Presence of local complications
GOALS OF PANCREATIC SURGERY:
– Removing pancreatic cysts or tumor
– Relieving pain
– Enhancing digestive function
-Preventing further decline of function
WHIPPLE PROCEDURE (Pancreaticoduodenectomy)
Tumors, cysts, and obstructions in the head of the pancreas are removed using the surgery known as the Whipple procedure.
A Whipple procedure is a treatment option for people whose pancreas, duodenum, or bile duct is affected by cancer or any other disorder.
In a classic Whipple procedure, the head of the pancreas, stomach and bile duct, and some of the small intestines are removed. The goal of doing a Whipple procedure for cancer is to remove the tumor and prevent it from growing and spreading to other organs.
In Pylorus – Preserving Whipple procedure, only part of the duodenum is removed and the pylorus (the part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum) is kept.
Read: Check out Latest Services
PARTIAL OR DISTAL PANCREATECTOMY
Tumors, cysts, and obstructions in the body or tail of the pancreas are removed using a procedure called a Distal Pancreatectomy. In this process, the affected portion of the pancreas, with or without the spleen is removed to complete the procedure.
TOTAL PANCREATECTOMY
In a total pancreatectomy, the entire pancreas is removed together with the duodenum, the Gallbladder and part of the bile duct, and the spleen.
It is done for removing centrally located, large or multiple tumors, severe chronic pancreatitis, and certain high-risk cystic diseases.
To complete the procedure the remaining bile duct and the stomach are reconnected to the small intestines.
POST-SURGICAL EXPERIENCE
Following surgery, you may lose certain body functions that were performed by the tissues and organs that were removed. But most of these losses can either be treated or managed.
After a Whipple procedure, there is usually no loss in functions associated with removing the gallbladder or a part of the bile duct.
However, sometimes, you may develop diabetes and may experience the presence of fat in stool called steatorrhea and a reduction in nutritional absorption.
Total pancreatectomy can be combined with transplantation of insulin-producing islets which are separated from the removed pancreas and transplanted into the liver. This additional procedure may reduce or eliminate the need for insulin injections.
BENEFITS OF PANCREATIC SURGERY:
This surgery can be performed safely and effectively and is well tolerated by patients.
The benefits of this surgery generally outweigh the functional losses associated with the removal of organ parts, which can be routinely and effectively managed.
With the advances in medical and patient care, this surgery has evolved into a safe procedure with low mortality rates.
For the best possible outcomes, seek out an experienced surgeon who specializes in Pancreatic Surgery.
Do not limit if you find any of the symptoms or signs related to your pancreas. If you are diagnosed with any of these symptoms, there are ways to treat the problem for the pancreas as soon as it gets detected. For treatment or to book an appointment contact us on: 0261 280 0000