CANCER is a word, not a SENTENCE!!
Most of us are in denial about the possibility of getting a disease called cancer.
And even if they think about it at all, they are more likely to worry about getting lung or breast cancer, than they are about cancer of the colon and rectum. Very few people are aware of Colorectal Cancer.
Colorectal cancer is common cancer worldwide with a majority of cases occurring in developed countries.
In India, the annual incidence rates for colon cancer and rectal cancer in men are 4.4 – 4.1 per 1,00,000 and 3.9 per 1,00,000 in women, respectively.
Colon cancer is one of the deadly forms of cancer, the reason being that it is detected late. But it’s one of the easiest and most curable cancers if it gets diagnosed at an early stage.
Read more about Dr. Dhaval Services
If you’ve been diagnosed with colorectal cancer, or are at risk for developing it, it’s time to know everything you can.
Understanding Colorectal Cancer
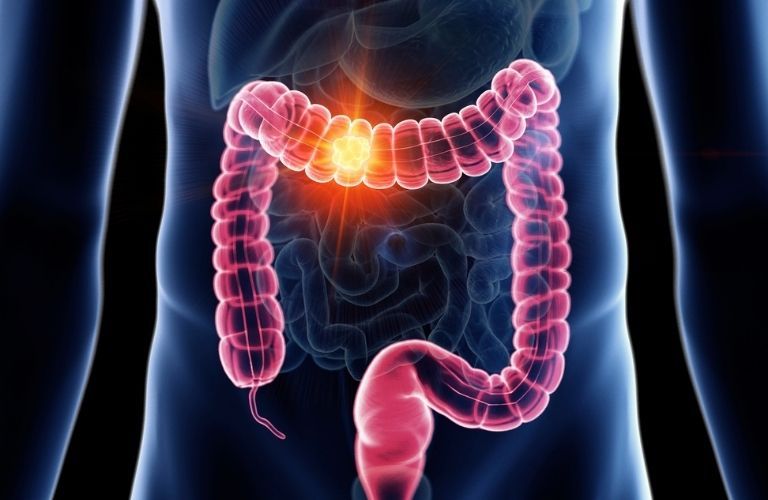
Cancer that develops in the large intestine is called Colorectal Cancer. Also known as bowel cancer, is cancer that affects the colon and rectum.
Colorectal cancer is a disease in which cells in the colon or rectum grow out of control or start dividing uncontrollably.
The colon is the large intestine or large bowel and the rectum is the part that connects the colon to the anus, the last part of the alimentary canal.
For more details Like and Subscribe Dr.Dhval YouTube Channel:
How Does Colorectal Cancer Start?
Most colorectal cancer starts in the small clumps of cells called Polyps. When the normal cells lining the colon and the rectum undergo changes, they start growing abnormally and uncontrollably forming polyps. These polys can grow bigger into the wall of the large intestine and turn into a cancerous tumor. But not all polyps change into cancerous ones, it depends upon the type of polyp it is.
How Dangerous Is Colorectal Cancer?
As with colorectal cancer, the longer the delay in treatment, the greater the danger. But when colorectal cancer is discovered early, it’s usually treatable and is not life-threatening.
But if it is not treated on time, the cancer cells can enter the bloodstream and spread to the nearby lymph nodes thus spreading to other organs over time.
Risk Factors Of Colorectal Cancer:
– Family History
– Colon Polyps
– Age 50 or Older
– Obesity
– Smoking
– Not Physically Active
– Too Much Alcohol
– Other Inflammatory Colon Diseases
Read Also: Colorectal Cancer
Symptoms Of Colorectal Cancer
It is often known to be a SILENT DISEASE.
It’s possible to have colorectal cancer without any symptoms, especially in the early stages.
For this reason, it is very important to have regular colorectal screenings if you are at known risk or if you experience the related signs to detect problems early.
Following are the common sign & symptoms experienced in colorectal cancer:-
● Change in bowel habits
● Blood in the stool
● Feeling unable to empty bowel
● Belly pain, bloating, or cramps
● Unexplained weight loss
● Feeling very weak or tired
● Vomiting
Diagnosis Of Colorectal Cancer
If you have the above signs and symptoms that might be from colorectal cancer, or if upon running screening tests, it shows something abnormal then your doctor will recommend one or more of the exams and tests below to find the cause.
A thorough examination of the colon and rectum is the only way to detect polyps or cancer. Your doctor will ask you about your medical history and will physically examine you in addition to running up other diagnostic tests.
Sigmoidoscopy
It is the minimally invasive examination of the large intestine from the rectum to the nearest part of the colon, the sigmoid colon. It explores the lower third of the colon
Colonoscopy
Examination of the inside of the colon using a colonoscopy, inserted into the rectum. A colonoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens attached to its one end for viewing. It can screen the entire colon.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope. Other tests can suggest that cancer is present, but only a biopsy can make a definite diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Blood Testing
Your doctor may run some blood tests to get a better idea of whatʼs causing your symptoms. Liver function tests (LFT) and Complete Blood Count (CBC) can rule out other diseases and disorders.
CT Scan
Colorectal cancer is sometimes initially discovered on CT scans when it gets detected to have spread to other organs and lymph nodes.
PET Scan
A PET scan is usually combined with a CT scan (see above), called a PET-CT scan.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Ultrasound
Biomarker testing of the tumor
Treatment Of Colorectal Cancer
In cancer care, different types of specialists often work together to create a patient’s overall treatment plan that usually includes or combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team.
For colorectal cancer, specialists include :
– Gastroenterologist
– Surgical oncologist
– Colorectal surgeon
– Radiation oncologist
– Medical oncologist
Factors that play an important role in determining your treatment plan may include your :
– Medical history
– Overall health
– Decisions concerning the side effects of each treatment option
Common Treatment Options Available For Colorectal Cancer
Surgery
Surgery is the most common colorectal cancer treatment. Surgery for colorectal cancer may involve removing tumors, removing the affected section of the colon, reattaching healthy ends of the intestines, and removing nearby lymph nodes.
Surgical Options for colorectal cancer include:
– Laparoscopic surgery
– Colostomy for rectal cancer
– Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or cryoablation
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy x-rays to destroy cancer cells. Sometimes radiation is combined with chemotherapy.
Therapies Using Medications:
– Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells, usually by keeping the cancer cells from growing, dividing, and making more cells.
– Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a treatment that targets cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival. This type of treatment blocks the growth and spread of cancer cells and limits damage to healthy cells.
– Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy also called biologic therapy, is designed to boost the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer cells.
There’s no CAN’T in Cancer, it’s a CAN. You can fight it, you can find a way through!
Keep calm and get your colonoscopy for early detection and effective treatment.
For More Details Book an Appointment Now or Call Us: +91 9909024259
Frequently asked questions
Q. What are the early signs of colorectal cancer?
Some early common warning signs of colorectal cancer are:
- Rectal bleeding, either bright or dark red.
- Change in bowel habits
- Having a feeling that you have to empty your bowel but nothing passes
- Anemia caused by iron deficiency
- Persistent abdominal pain, gas
- Unexplained weight loss
Q. How serious is colorectal cancer?
If a doctor catches cancer while it’s still confined to the outer lining of the colon or rectum, you can probably look forward to a full recovery. If cancer spreads to the muscle of the colon or rectum, you have a 75 percent chance to live at least another five years. Cancer can spread to the liver, bones, or lungs in the worst-case scenario.
Q. What causes colorectal cancer?
Researchers have found several factors that can increase a person’s risk of colorectal cancer, but it’s not yet clear exactly how all of these factors might cause this cancer.
Risk factors associated with colorectal cancer include:
- Family history of colorectal cancer
- Being overweight or obese
- Not being physically active
- Certain types of diet
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
Q. Is colorectal cancer curable?
Colorectal cancer is a highly treatable and often curable disease when localized to the bowel. Surgery is the primary form of treatment and results in a cure in approximately 50% of the patients. Recurrence following surgery is a major problem and is often the ultimate cause of death.
Q. How does colorectal cancer spread?
Colorectal cancer usually begins as a benign polyp that develops in the inner lining of your rectum or colon. If this polyp develops malignancy, it can grow further into the wall of your colon or rectum and invade the blood or lymph vesselsColorectal cancer cells can also break away from the main tumor and can travel through the blood or lymph system to other parts of the body, including the liver, lungs, and brain.