Gall Bladder Surgery in Surat
Gall Bladder Function
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped sac located beneath the liver. It stores bile which was produced by the liver. Bile is a greenish yellow, sticky fluid. Bile helps in digestion by making cholesterol, fats, and fat-soluble vitamins easier to absorb from the intestine. The biliary tract consists of small tubes (ducts) that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and then to the small intestine. Read and know in brief about gall bladder and basic of Gall Bladder Surgery in Surat.
Gall Bladder Stones
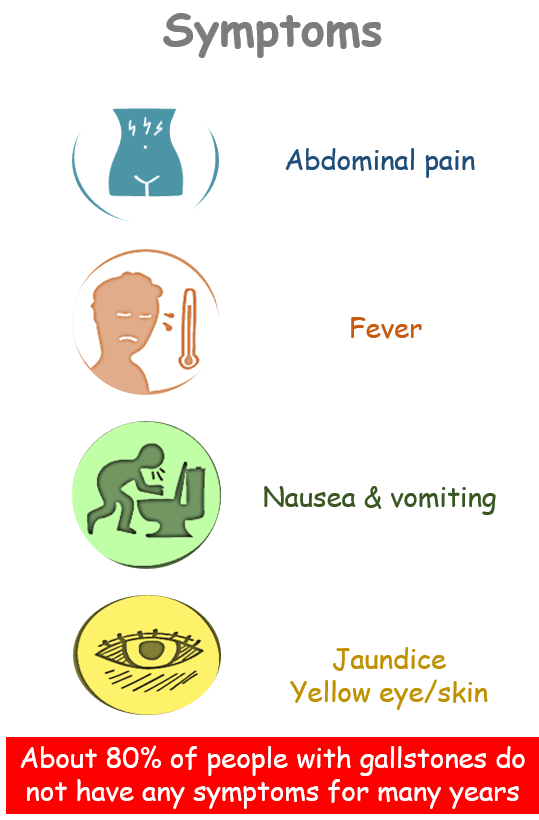
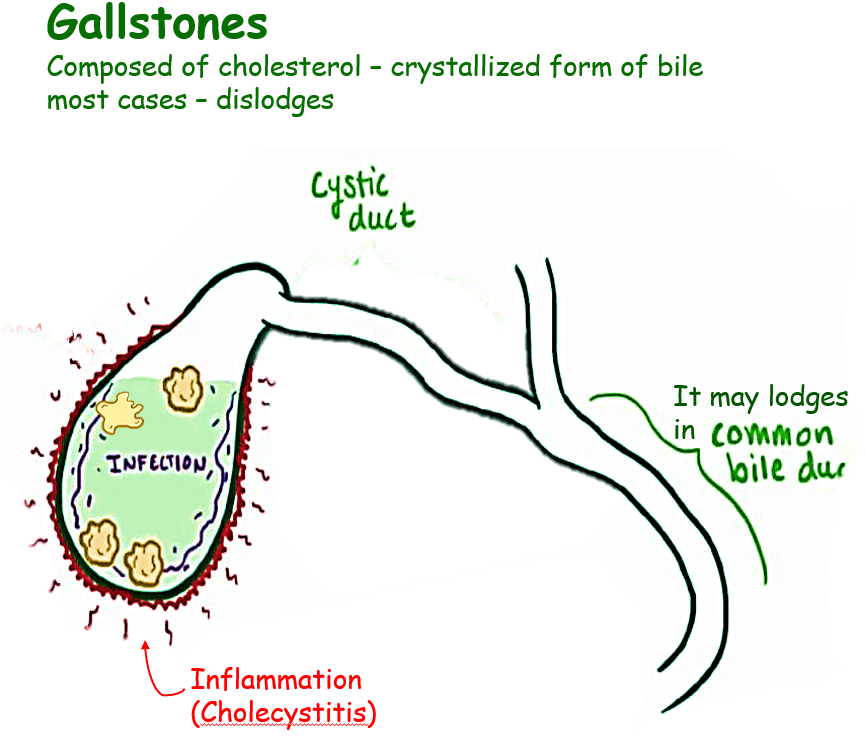
Gall bladder localised in the upper abdomen, usually on the right side under the ribs. Location is hard to pinpoint, particularly for people with diabetes and older people. Gall Bladder surgery done most commonly for stones are usually composed of cholesterol that has crystallized from bile. They form in the gallbladder. About 80% of people with gallstones do not have any symptoms for many years, but if they leave the gallbladder and lodge in the cystic duct, the common bile duct, or the ampulla of Vater then it causes pain. People often feel nauseated and vomit. If the blockage persists, the gallbladder becomes inflamed (a condition called acute cholecystitis), causes fever. Blockage of the common bile duct or the ampulla of Vater can cause the ducts to widen (dilate). It can also cause fever, chills, and jaundice (a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes). Stones that block the ampulla of Vater also can block the pancreatic duct, causing inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), as well as pain. Gallstones can erode the gallbladder wall, sometimes resulting in a hole (perforation).
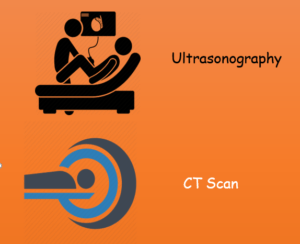
Ultrasonography is essential. It is 95% accurate in detecting gallstones in the gallbladder. Other diagnostic tests include Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). If results of these imaging tests are unclear, endoscopic ultrasonography may be done better than standard ultrasonography. Blood tests used to evaluate liver functioning.
Treatment for Gall Bladder Stones
If gallstones cause disruptive, recurring episodes of pain, a doctor may recommend surgical removal of the gallbladder(cholecystectomy). No special dietary restrictions are required after surgery. About 90% of cholecystectomies are done using a laparoscope. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has lessened the discomfort after surgery, shortened the length of hospital stays, provided better cosmetic results, and reduced the time needed to recover. Dr Dhaval Mangukiya with vast experience for Gallbladder Surgery in Surat available at SIDS Hospital for his expert advice and solutions.

At SIDS Hospital
Our expert team of surgeons are performing maximum number of gall bladder surgery in south gujarat for gallbladder diseases, Biliary diseases and cancer with most advanced laparoscopic instruments. SIDS Hospital is equipped with the most advanced set up of endoscopic instruments to diagnose and treat the biliary problems where we are performing more than 7000 procedures in a year by our panel of the most experienced endoscopists.